order shipments

Order Shipments are sourced from existing sales orders and remove the
product from inventory.
A Sales Order
must be created prior to creating an order shipment.
The following procedures are outlined in the Order Shipment document:
Create an Order Shipment
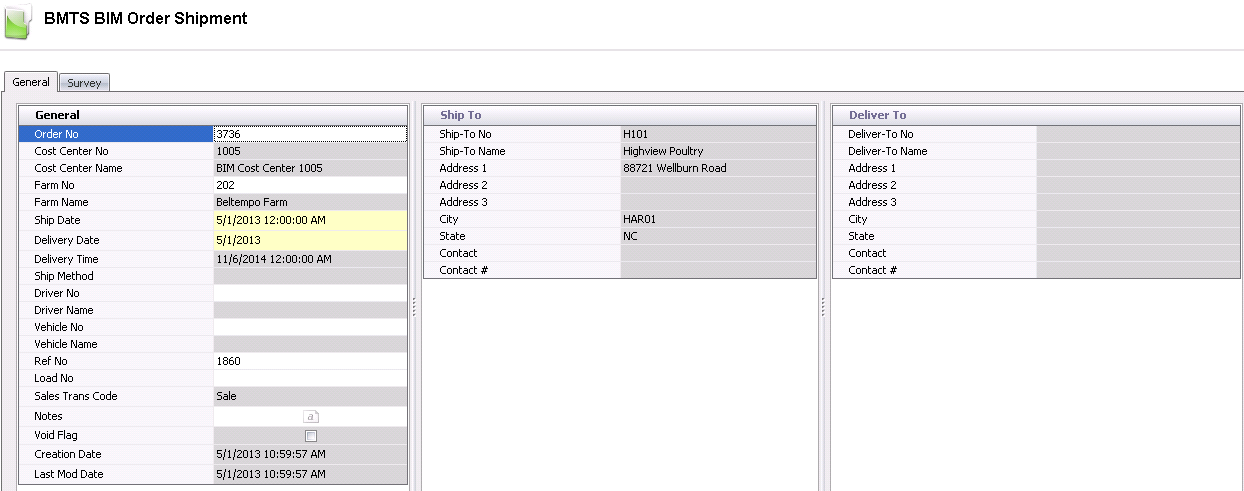
General
The General tab contains the following components:
Order Shipment Header
The order shipment header contains the base data to outline the shipment.
The header is divided into three sections to group the data. Most of the
information defaults in and is derived from the associated sales order.
- In BMTS>BIM>Transactions,
select Order Shipments.
- In the Order
Shipment main index, click
 to create a
new order shipment.
to create a
new order shipment.
General
- Click on the General
tab.
- From the Order
No drop-down menu, select the sales order to be shipped. Order
No is an auto-assigned unique number that was assigned to the
order when it was initially created.
- Cost Center No
will default in and indicates the cost center from where the product
will be shipped.
- Cost Center Name
will default in and displays the name of the cost center.
- From Farm No,
select the farm from where the product will be shipped.
- Farm Name
will default in and displays the name of the farm.
- Enter the Ship
Date to indicate the date that the product will be shipped.
- Enter the Delivery
Date to indicate the date the product will be delivered.
- Delivery Time
will default in with no option to modify.
- Ship Method
will default in if applicable, with no option to modify.
- Driver No
is an optional field to identify the driver who will be transferring
the product. Drivers must be set up prior in: Admin>Business>General>Definitions>Drivers.
- Driver Name
will default from Driver No and displays the name of the driver.
Vehicle
No is an optional field to identify the vehicle used to transfer
the product. Vehicles must be set up prior in: Admin>Business>General>Definitions>Vehicles.
Vehicle
Name will default from Vehicle No and displays the name of
the vehicle.
Ref
No is a unique reference number that identifies the order shipment
transaction. This can be manually or automatically entered.
Load
No is an optional field to enter the load number of the shipment.
Sales
Trans Code identifies the type of sales transaction and will
default to Sale.
In the Notes
field, enter any additional information relating to the order shipment.
Selecting the Void flag will cancel the order
shipment.
Creation
Date indicates the date the transaction was created.
Last
Mod Date indicates the date the transaction was last modified.
Ship To
The Ship-To tab contains the base data for the ship-to customer. The
details in the tab will default in from the sales order with no option
to modify.
- Ship-To No
displays the code that is used to identify the ship-to customer.
- Ship-To Name
displays the name of the ship-to customer.
- Address 1-3
fields display the address details of the ship-to customer.
- City displays
the city in which the selected ship-to customer is located.
- State
displays the state in which the selected customer is located.
- Contact
defaults from the primary contact defined on the Ship-To customer.
- Contact #
defaults from the Ship-To customer and displays the main contact telephone
number, if applicable.
Deliver
To
The Deliver-To tab contains the base data for the deliver-to customer.
This tab will be populated if the deliver-to customer is set up in the
Business Usages tab of Customers.
The details in the tab will default in from the sales order with no option
to modify.
- Deliver-To No
displays the code that is used to identify the deliver-to customer.
- Deliver-To Name
displays the name of the deliver-to customer.
- Address 1-3
fields will default in and display the address details of the deliver-to
customer.
- City displays
the city in which the selected deliver-to customer is located.
- State
displays the state in which the selected customer is located.
- Contact
defaults from the primary contact defined on the Deliver-To customer.
- Contact #
defaults from the Deliver-To customer and displays the main contact
telephone number, if applicable.
Order
Shipment Details
The lines and fields in the Details tab will default from the selected
sales order.

- Line Index
identifies the line number of the order.
- Sales SKU No
identifies the product that is being shipped.
- Sales SKU Name
displays a description of the product being shipped.
- Complex Entity
No displays the entity number of the farm.
- Cost Center No
indicates the cost center where the product is being shipped from.
Cost Center
Name defaults from Cost Center No and displays the name of
the cost center.
- Quantity Ordered
displays the number of units ordered that are requested to be shipped.
- Quantity Shipped
displays the quantity of units that were actually shipped. This field
will be populated when the product inventory is selected.
- Variance
will be automatically calculated and displays the difference in unit
amounts between Quantity Ordered and Quantity Shipped, if applicable.
- The Complete
flag is selected if the order shipment is complete and shipping has
been completed.
- If the order was not completely shipped, but the
remaining quantity will be shipped on another shipment, select the
Back Order flag. For example,
if 1000 units were ordered, but only 750 are available to be shipped
today, and the remaining 250 will ship tomorrow, then the back order
flag should be selected. On the other hand, if only 750 units are
available to be shipped and the remaining 250 units will never be
shipped, the back order flag should be left de-selected.
- Allow
Any % Over defaults
as a read-only field from the product and lets the user know if additional
quantities from the order quantity can be shipped. If this flag is
selected, there
is no limit on the product amount and the customer can be shipped
any quantity over the specified product units.
- Max
% Over defaults
as a read-only field from the product and is
used when the product has a tolerance percentage for the order shipment.
(Example: The order shipment has 100 units. Max % Over is defined
as 5%, which means the receiving transaction will allow up to an including
5 additional units).
Additional Details
Within the Details tab, there
is a child grid to add additional details relating to the order shipment.
The child grid section is
comprised of three tabs:
- Click
 on the Line Index tab
to display the child grid.
on the Line Index tab
to display the child grid.
- Click
 to add a new item line.
to add a new item line.
- The Select Entities for Shipment dialog box will
appear with all available entities.
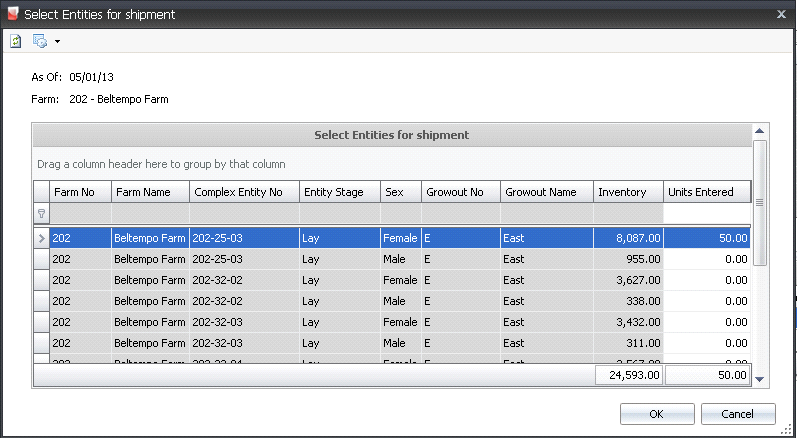
- Select the required Complex Entity No and
in the Units Entered
field, enter the number of units to be shipped.
- Click 'OK'.
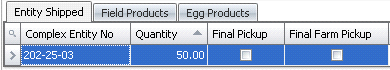
- Complex Entity
No displays the entity where the product is shipped
from.
- Quantity
displays the number of units shipped.
- Select the Final
Pickup flag if this is the last pick-up of the product at the
farm.
- Select the Final
Farm Pickup flag if the final pick-up from the farm has been
completed.
Field products can be added when selling
a field product, such as medication, vaccination, or miscellaneous supplies.
- Click
 to add a
new line item.
to add a
new line item.
- In the pop-up dialog box, select the required
field product and in the Units
Entered field, enter the number of units to be shipped.
- Click 'OK'.
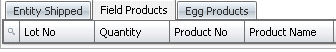
- Lot No
is a unique identification number for the field product, and is optional.
- Quantity
displays the amount of field product units that are being shipped.
- Product No
displays the code for the field product.
- Product Name
defaults from Product No and displays a description of the product.
Egg products can be added if the user is
selling eggs (hatching eggs) to a customer.
- Click
 to add a
new line item.
to add a
new line item.
- In the pop-up dialog box, select the required
egg product and in the Units
Entered field, enter the number of eggs to be shipped.
- Click 'OK'.

- Complex Entity
No displays the entity number of the farm where the egg products
are coming from.
- Eggs displays
the number of eggs to be shipped.
- Production Date
indicates the date the product was produced.
- Average Age
displays the average age of the eggs.
- Breed No
indicates the breed of the product that is being shipped.
- In the Hatch
Date field, enter the date the chicks are expected to hatch.
- In the Percent
Hatch field, enter the percentage of chicks expected to hatch
from the eggs shipped.
- In the Percent
Fertility field, enter the percentage of eggs with embryos,
or the percentage of fertile eggs.
Product No
indicates the required egg product.
- Product Name
displays a description of the egg product.
Survey
Survey Codes are set up in: Admin>Business>General>Order
Management>Survey Codes. The codes are then displayed on
the Order Shipment tab, where the user enters a value from 1 (lowest)
to 10 (highest). The system will calculate an average score for the shipment.

Post
an Order Shipment
Once the order shipment has been created and saved, the shipment needs
to be posted. The posting process locks the order shipment to prevent
edits, and creates the journal transaction to record the receivable and
revenue accrual. If internal pricing is used, the credit to inventory
and debit to cost of sales will be recorded using the internal price and
adjusted to actual at period end. The UnPost option unlocks the order
shipment transaction and reverses the journal transactions.
- In the Order Shipments main index, select the
required order shipment transaction and right-click to select 'Post'.
Alternatively, click the green check mark
 in the
top menu bar and select 'Post'.
in the
top menu bar and select 'Post'.
- To un-post an order shipment, select the required
order shipment and right-click to select 'Unpost'. This process
will set the transaction status to 'Reversed' status, which allows
the transaction to be edited.
Journal Transaction
The posting process creates the journal transaction. The journal will
accrue the sales revenue and accounts receivable based on the values that
are defined in the sales order. The posting process will also credit the
inventory for the cost of the product and debit the cost of sales based
on the internal price defined. The period end
process reverses the internal price and records the actual cost of the
product.
![]()
 to create a
new order shipment.
to create a
new order shipment.

 to add a new item line.
to add a new item line. 

 to add a
new line item.
to add a
new line item.
 to add a
new line item.
to add a
new line item.

 in the
top menu bar and select 'Post'.
in the
top menu bar and select 'Post'.